Past Tense Present Tense Future Tense
(She read) (She reads) (She will read)
↑ ↑ ↑
Tense Usage Example
Present Simple Habits, general truths, routines He works at a bank.
Present Progressive Ongoing actions at present Ravi is eating right now.
Present Perfect Actions completed at an unspecified time I have seen her last night.
Present Perfect Progressive or Continuous Ongoing actions that started in the past and continue We have been waiting for an hour.
Past Simple Completed actions at a specific past time Jenifer visited Paris last summer.
Past Progressive Ongoing actions at a particular past time I was sleeping when the phone rang.
Past Perfect Actions completed before another past action He had already left when I arrived.
Past Perfect Progressive or Continuous Ongoing past actions before another past event She had been studying for hours before the test.
Future Simple Future predictions, plans, or promises Keven will go to the party tomorrow.
Future Progressive Ongoing actions at a future time We will be working at 3 PM.
Future Perfect Actions completed before a future time I will have finished by next week.
Future Perfect Progressive or Continuous Ongoing future actions until a specific time, focusing on duration In 2025, they will have been living here for ten years.
The depth of Tenses in English grammar refers to how actions or states in relations to time are represented. As a rule English Tenses are classified into mainly three general types:
-
- Present Tense
-
- Past tense
-
- Future Tense
All the above English Tenses mentioned above are further subdivided into four types, they are as below:
-
- Simple tense
-
- Progressive or Continuous
-
- Perfect
-
- Perfect Progressive or Continuous
The Present Tense in English are used to describe current situation that are happening general truth, actions or states of being. And also refer to actions that are schedule to happened near in the future.
Table of ContentsTenses In English
Present Tenses
Tenses
Used For
Examples
Present Simple
Used for general truths, habits and regular actions
He reads magazine every morning
The sun sets in the west
Present Progressive or Continuous
Actions happening right now or around the present time
Lucus is reading a book right now.
We are studying for exams
Present Perfect
Actions that have occured at an unspecific time or have relevance to the present
He has finished her homework
She has lived in Germany for seven years.
Present Perfect Progressive or Continuous
Actions that started in the past and continue into the present ,emphasizing the duration.
He has been doing this work for two hours
They have been working on this project all day.
The Past Tense is used to describe actions or situations that happened before the present time shows the actions has already been completed. In some cases past tense describes an ongoing or you can say repeated actions in the past. The past tense is essential for narrating any events, describing stories and explaining what has happened in one’s personal life.
Tenses In English – Past Tense
Past Tenses
Tenses
Used For
Examples
Past Simple
Used for completed actions that happened at a specific time in the past
He read this magazine in the morning
We visited the museum last week
Past Progressive or Continuous
Actions that were in progress at a particular moment in the past.
She was reading when the phone rang
We were studying for exams when our friends came in the room
Past Perfect
Actions that were completed before before another actions in the past
He had left room before i arrived
We had finished our work by the time i called
Past Perfect Progressive or Continuous
Actions for actions that were ongoing in the past before another past event, focusing o duration.
He had been doing this work for two hours when i called him
They had been working on this project all morning before the meeting
The Future Tense actually used for describe events or actions that will happen after the present moment. The Future tense mainly used for plans, predictions, any intentions and any future events.
Tenses In English – Future Tense
Future Tenses
Tenses
Used For
Examples
Future Simple
Used for actions that will happen in the future
I will go to super market tomorrow
I will visit my father next month
Future Progressive or Continuous
Actions that will be completed before a specific point in the future
We will be studying at 6pm
She will be traveling to Germany next month
Future Perfect
Actions that will be completed before a specific point in the future
I will have finished the project by the next year
He will have graduated by this time we arrive
Future Perfect Progressive or Continuous
Actions that will be ongoing until a certain point of time in the future focusing on duration.
By the next week ,we will have bee working here for seven years.
In one month they will have been living in this city for a decade
Simple PRESent – At glance
When to use simple present
Verb “to be” in the present simple
Verbs in the 3rd person singular and their pronounciation
How to make sentences in the present simple
Table of contents
-
- When Do we Use ?

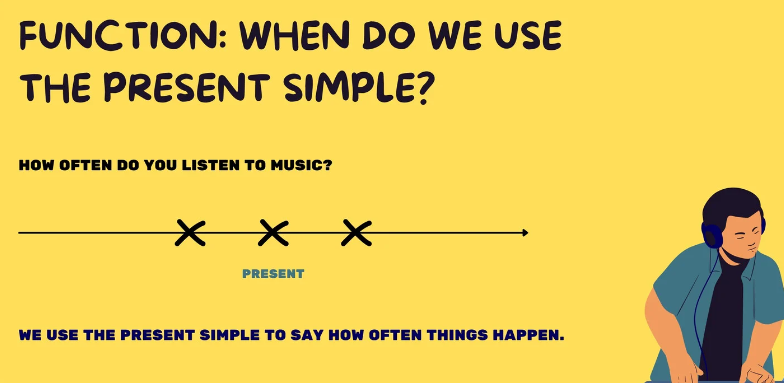
We use Present Simple to say that something happens always and repeatedly.
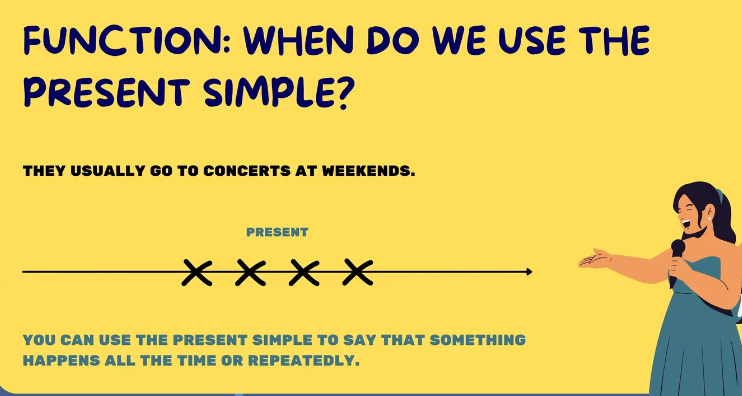
We use Present Simple to say the things happen often
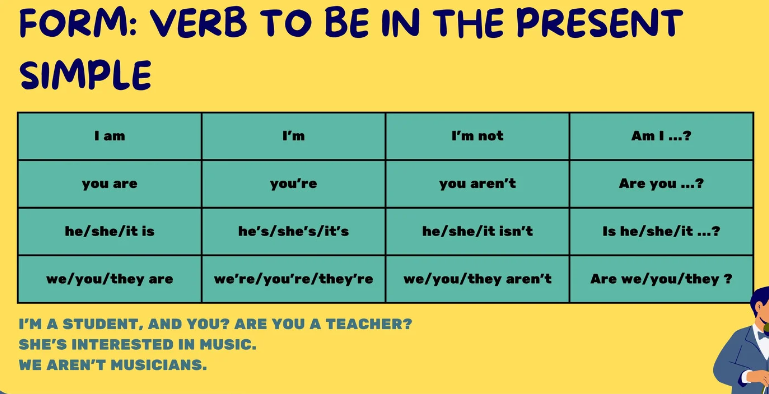
Use of VERB TO BE –am, is, are
Example :
- I am – i’m
- You are – You’re
- He is – he’s
- She is – She’s
- They are – they’re
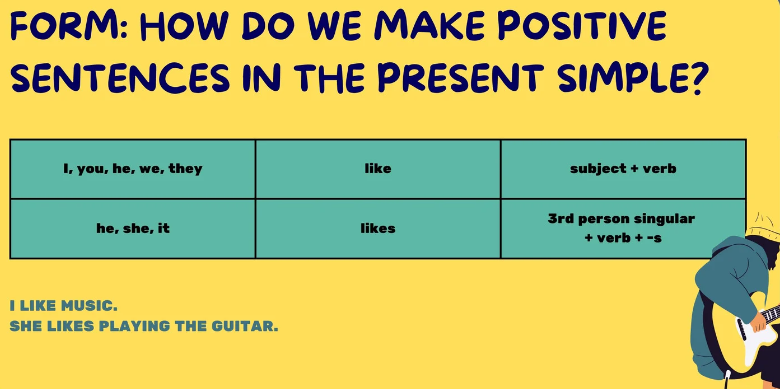
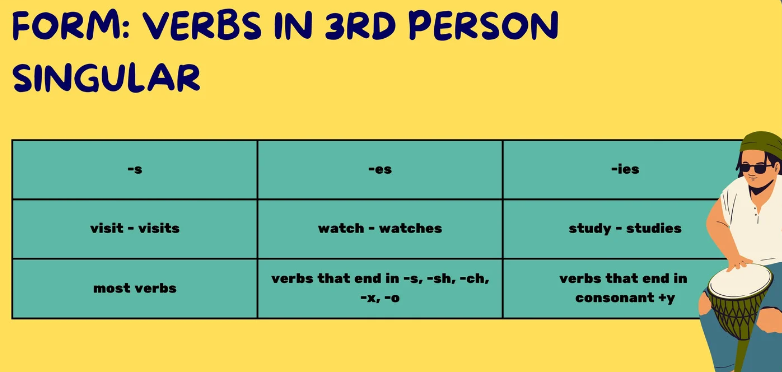


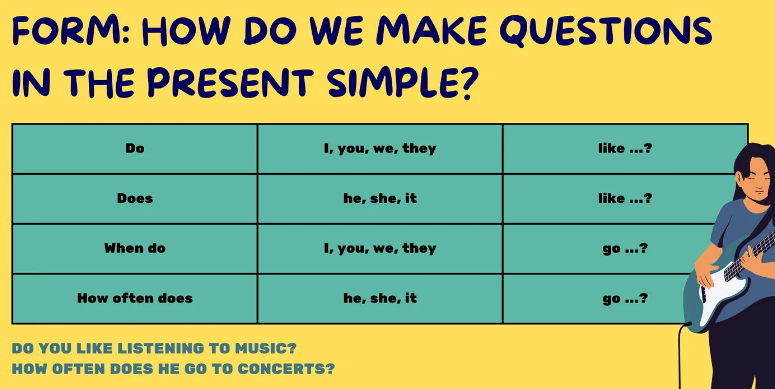





Simple past
Uses of the Simple Past Tense
- Expressing Completed Actions ( I visited my grandfather last weekend)
- Talking about Past Habits or Routines (I used to play soccer every Sunday)
- Narrating Past Events (Once upon a time, there was a brave Knight)
- Describing Past States or Conditions ( She was tired after a long at work)
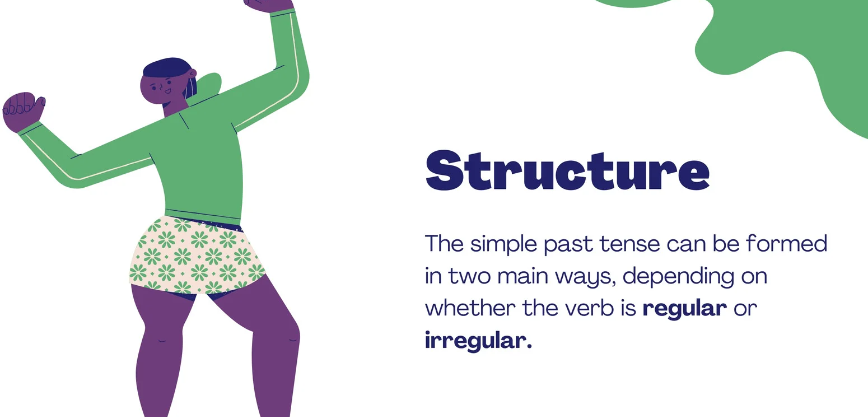
Structure
- Regular Verbs : Regular verbs follow a consistent pattern in past tense by adding ( -ed ) to the base form of verb.
- affirmative ( + )
- Subject + Verb (base form + -ed ) + object
- negative ( – )
- Subject + did not + verb ( base form ) + object
- Interrogative ( ? )
- Did + subject + verb (base form ) + object?
List of Regular Verbs here
2.Irregular Verbs : Irregular verbs do not follow the consistent pattern, form vary need to be memorized.
- Affirmative ( + )
- Subject + irregular verb ( V2 ) + object
- negative ( – )
- subject + did not + verb (V1 ) + object
- Interrogative ( ? )
- Did + subject + verb ( V1 ) + object ?
- Stop – Stopped
- Walk – Walked
- Dance – Danced
- Cook – Cooked
- I cooked chicken for dinner last night
List of Irregular Verbs Here
Past time Expressions
- yesterday : We went to the park last night
- Last (day/week/month/year) : He traveled to Germany last month
- In (year/decade/century) : i was born in 1990
- Ago ( a week/two days/ a year) : she got married a year ago



Simple Future
Simple Future are used to express actions that will happen in the future. They can be formed using like “will” and “ne going to”. We use future tense when we want to make predictions, talk about planned events, or express any intentions.
Structures and examples
- Affirmative (+)
- subject + will/shall + V ( base form)
- Ex : I will go to Spain
- subject + will/shall + V ( base form)
- Negative (-)
- subject + will not / won’t + V(base form)
- I will not go to Spain
- subject + will not / won’t + V(base form)
- Interrogative ( ?)
- Will + subject/pronoun + V1 + objects
- Will you join us later
- Will + subject/pronoun + V1 + objects
Time Expression
We usually use the following time expression with the Future simple Tense
- Tomorrow
- Next ( week/month/year)
- in ( a minute/ an hour)
- soon
- Later
Be Going To
We use “be going to” to express plans, intentions, and predictions based on present evidence or intentions
- He’s going to do exercise tomorrow morning (intentions)
- We are going to start a new project next month.(plan)
- Look at those clouds! i think it’s going to rain ( prediction based on evidence)